ONL Therapeutics Advances Xelafaslatide Phase 2 Trial for Geographic Atrophy Treatment
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
This analysis is based on the ONL Therapeutics announcement [1] published on October 28, 2025, regarding the randomization of the first patient in the global Phase 2 GALAXY trial evaluating xelafaslatide for geographic atrophy treatment.
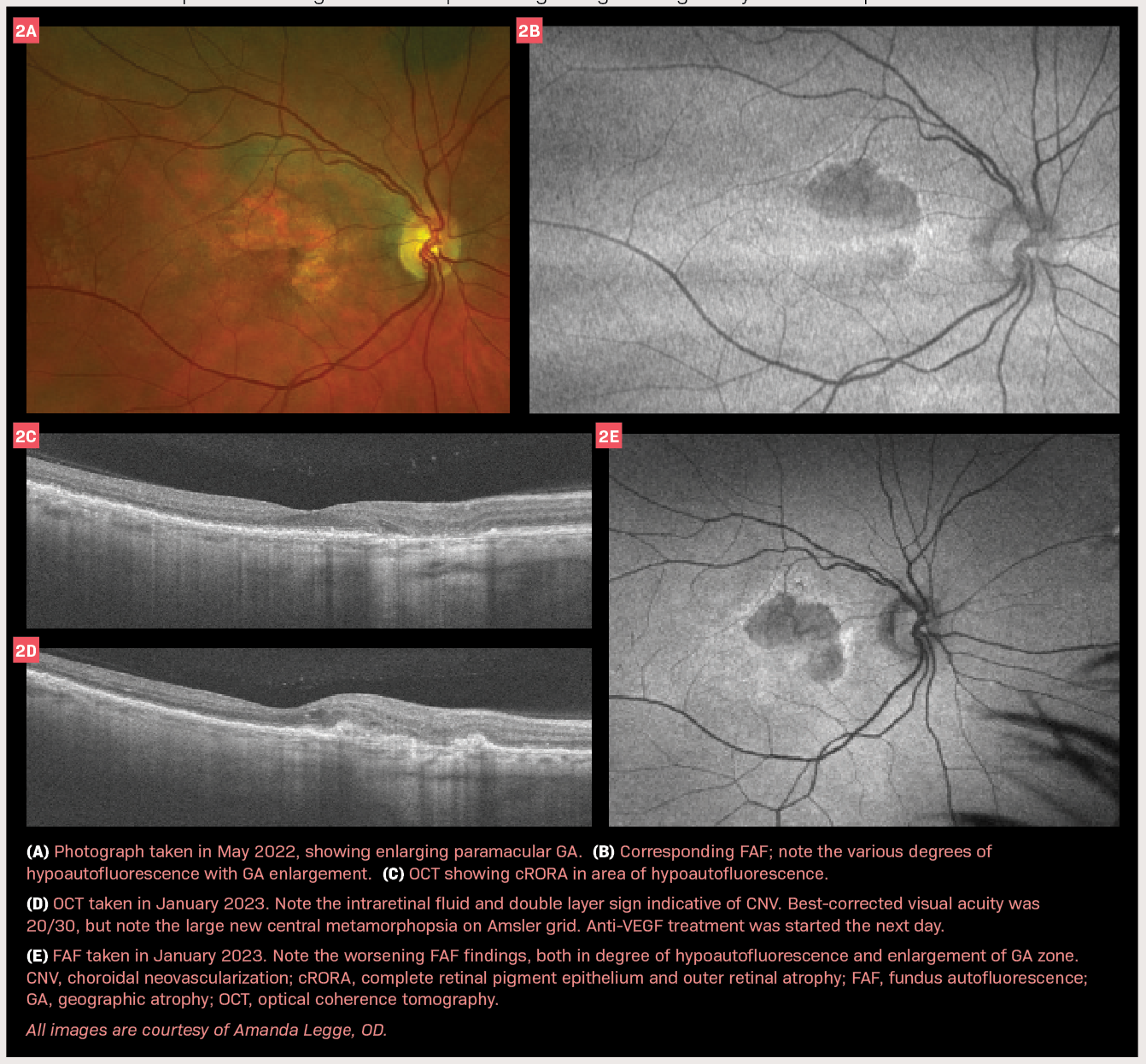
ONL Therapeutics has achieved a significant clinical development milestone with the randomization of the first patient in its Phase 2 GALAXY trial for xelafaslatide (ONL1204) in patients with geographic atrophy (GA) associated with dry age-related macular degeneration [1]. This progression follows recent regulatory approvals from the World Health Organization and the United States Adopted Names Council establishing “xelafaslatide” as the official nonproprietary name for ONL1204 Ophthalmic Solution [1].
The therapeutic represents a first-in-class approach through its Fas receptor inhibition mechanism, fundamentally differentiating it from current FDA-approved GA treatments that target complement proteins [1]. Xelafaslatide functions as a small peptide designed to protect retinal cells from apoptosis by blocking Fas activation at the receptor level, thereby preventing downstream death pathways and inflammatory cascades [3]. This neuroprotective strategy contrasts with the inflammation-focused approach of existing complement inhibitors [2].
The Phase 2 GALAXY trial is evaluating two dosing frequencies (every 12 weeks and every 24 weeks) at dose levels of 100 µg and 200 µg over a 72-week treatment period [2]. This extended dosing schedule could substantially reduce treatment burden compared to current approved therapies requiring administration every 25-60 days [4]. Previous Phase 1b results demonstrated that xelafaslatide was generally safe and well-tolerated, with efficacy signals showing slowed GA lesion growth compared to untreated eyes after 6 months [2].
Xelafaslatide represents a potentially significant advancement in GA treatment through its innovative Fas inhibition mechanism and extended dosing intervals. The therapy targets approximately 5 million individuals globally affected by GA, including 1.5 million in the United States [4]. GA accounts for roughly 25% of legal blindness cases in the United Kingdom and 20% of cases in North America, highlighting the substantial unmet medical need [4].
The Phase 2 GALAXY trial marks a critical development milestone that could position ONL Therapeutics as a meaningful competitor in the rapidly growing GA market. The product’s differentiated approach offers potential advantages including less frequent dosing (every 3-6 months versus monthly or bimonthly for current therapies) and a novel neuroprotective mechanism [1]. However, commercial success will depend on demonstrating robust clinical efficacy and maintaining a favorable safety profile through the remainder of clinical development.
With the GA market projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2029 [5], xelafaslatide has significant commercial potential if it can successfully navigate the regulatory pathway and establish competitive differentiation in an increasingly crowded therapeutic landscape. The therapy’s success would also validate the Fas inhibition platform for broader retinal disease applications, potentially creating additional value opportunities for ONL Therapeutics’ pipeline development.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
