Persistent Impact of 2025 U.S. Tariff Hikes on Global Growth and Industry Dynamics
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
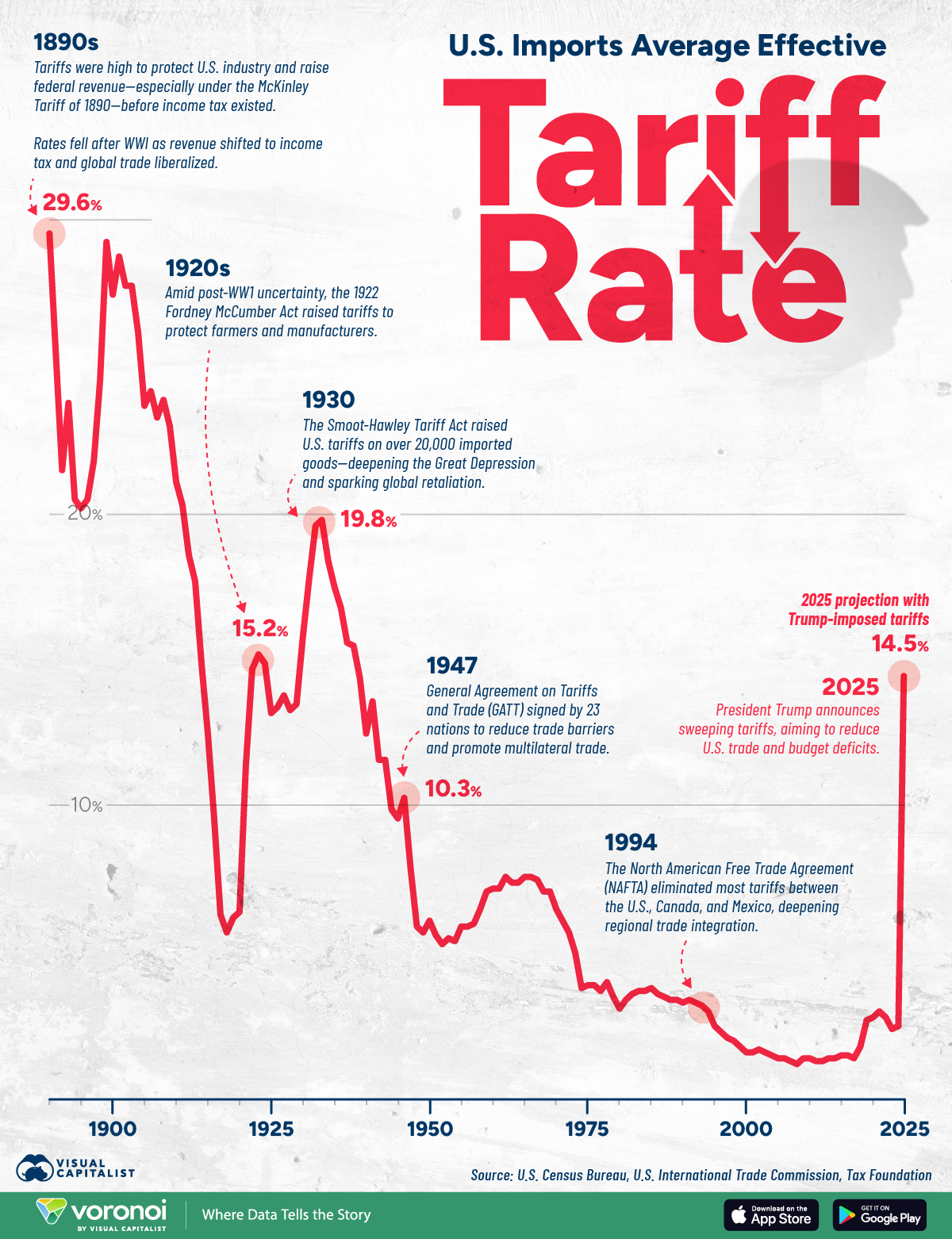
In early 2025, the U.S. implemented reciprocal tariffs targeting sectors like automotives, basic/fabricated metals, batteries, and technology products. By April 2025, the weighted-average tariff rate rose from ~2% to over 20%—the highest level since 1909 [1]. Trading partners responded with retaliation (China imposed 125% tariffs on select U.S. imports) and negotiations (75+ countries sought talks) [1]. The WSJ article’s core claim (persistent lingering impact) reflects ongoing macroeconomic and supply chain adjustments to these tariffs.
- GDP Growth: J.P. Morgan revised 2025 U.S. real GDP growth to 1.6% (0.3% below prior estimates) due to tariffs, retaliation, and policy uncertainty [2]. Global growth is projected to slow in H2 2025 [2].
- Inflation: Tariffs contribute to inflationary pressures; Yale’s Budget Lab estimates a 20+ percentage point increase in average tariff rates, pushing levels to 1909 highs [3]. Consumers may frontload spending in 2025, but purchasing power erosion will slow 2026 growth [3].
- Supply Chains: Modern supply chains amplify tariff impacts—rising import tariffs reduce exports (per Handley et al., 2025) [4]. Sectors relying on cross-border inputs (tech, manufacturing) face elevated costs [1,4].
Lack of clarity on long-term tariff frameworks weighs on business/consumer sentiment, leading to equity market declines and U.S. dollar weakening since February 2025 [3].
- Winners: Domestic producers in protected sectors (steel, aluminum) benefit short-term, but gains are offset by retaliatory barriers for exporters [1,4].
- Losers: Firms that are both importers and exporters (a large share of U.S. businesses) face disproportionate harm [4, citing Jensen 2016]. Tech and automotive sectors (with global supply chains) are particularly vulnerable [1].
- Barriers: Higher tariffs increase entry barriers for foreign firms into U.S. markets, while retaliation raises barriers for U.S. firms abroad [1].
- Supply Chain Adaptation: Firms accelerate reshoring/friendshoring to mitigate costs, shifting competitive dynamics to regions like Southeast Asia and Mexico [2,4].
- Tariff Revenue: The U.S. collected over $158 billion in tariff revenue by September 2025 [5], though this comes at the cost of slower growth [2].
- Recession Risk: J.P. Morgan puts 2025 recession probability at 60% (linked to tariffs) [4].
- Policy Uncertainty: Ongoing lack of tariff clarity hinders investment recovery [3].
- Retaliation Spiral: China’s 125% tariffs risk escalating trade tensions, while 75+ countries negotiate to reduce impacts [1].
- Consumers: Face higher prices for imported goods and reduced purchasing power [3].
- Businesses: Need to adjust supply chains, manage cost increases, and navigate retaliatory barriers [1,2,4].
- Governments: Balance tariff revenue gains against economic slowdown, inflation, and diplomatic tensions [5,2].
- Investors: Confront volatility and sector-specific risks (e.g., tech vs. domestic manufacturing) [3,2].
- Tariff Persistence: Lingering impacts (per WSJ) require long-term strategic adjustments.
- Retaliation Responses: Trading partners’ choices (negotiation vs. retaliation) will shape sector outcomes [1].
- Policy Clarity: Resolving tariff framework uncertainty is critical for investment recovery [3].
- Supply Chain Resilience: Speed of reshoring/friendshoring efforts determines competitive advantage [2,4].
- Inflation Management: Central bank responses to tariff-induced inflation will impact borrowing costs [3].
[1] McKinsey & Company. Tariffs and global trade: The economic impact on business. URL: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/geopolitics/our-insights/tariffs-and-global-trade-the-economic-impact-on-business (2025).
[2] J.P. Morgan Global Research. US Tariffs: What’s the Impact?. URL: https://www.jpmorgan.com/insights/global-research/current-events/us-tariffs (2025).
[3] Deloitte. Tariffs will impact the economy … and so will uncertainty. URL: https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/economy/spotlight/united-states-tariffs-impact-economy.html (11 April 2025).
[4] CEPR. The aftermath of tariffs. URL: https://cepr.org/voxeu/columns/aftermath-tariffs (2025).
[5] Wall Street Journal. Trump’s Tariffs Are Raking in Billions. Where Does It All Go?. URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w2HBhjcAtLM (12 September 2025).
Note: The original WSJ article (event source) was not fully crawlable, but its core claim (lingering impact) is supported by the cited sources.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
