Federal Reserve Ends Quantitative Tightening Early: Market Liquidity Boost Analysis
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Related Stocks
This analysis is based on the MarketWatch report [1] published on November 1, 2025, which detailed the Federal Reserve’s accelerated timeline to end quantitative tightening.
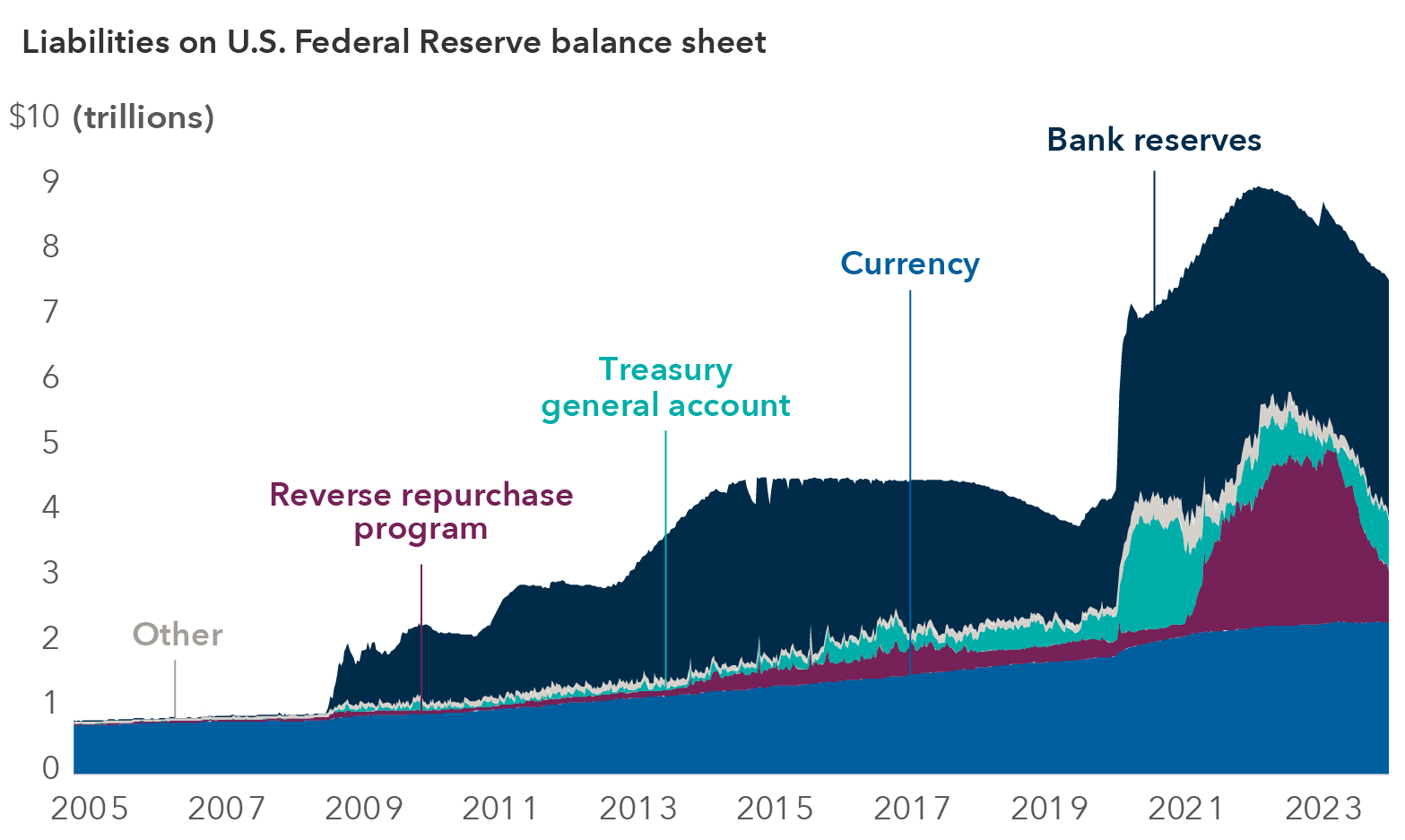
The Federal Reserve’s announcement to end quantitative tightening (QT) on December 1, 2025, represents a significant monetary policy shift that occurred earlier than market expectations of January-April 2026 [1]. This decision, announced alongside the Fed’s quarter-point interest rate cut on October 29, 2025, constitutes dual forms of monetary easing that will substantially increase financial market liquidity [1].
- Inflationary Pressures:Increased liquidity could reignite inflation concerns, particularly as long-term Treasury yields have been rising despite recent rate cuts [1]
- Market Dependence:Markets may become overly dependent on Fed liquidity support, potentially creating moral hazard and reducing price discovery efficiency
- Policy Credibility:Rapid policy shifts could impact Fed credibility if perceived as reactive rather than strategically planned
- Liquidity-Sensitive Sectors:Financial Services, Real Estate, and Communication Services showed immediate strength and may continue benefiting from increased liquidity [0]
- Treasury Market Efficiency:The Fed’s T-bill purchases should improve market functioning and potentially reduce short-term rate volatility
- Risk Asset Support:The liquidity injection provides a backstop for risk assets, potentially supporting equity market stability
- Treasury auction demand and pricing following the November 5 refunding announcement
- Banking sector liquidity indicators and credit market conditions
- Inflation data trends, particularly core measures excluding volatile components
- Money market fund flows and short-term funding market functioning
The Federal Reserve’s decision to end quantitative tightening on December 1, 2025, represents a significant monetary policy shift that will inject substantial liquidity into financial markets [1]. This policy change, combined with recent rate cuts, provides dual forms of monetary easing that support market functioning and risk asset valuations. The accelerated timeline suggests potential concerns about underlying financial system conditions that warrant careful monitoring.
Market response has shown sector rotation toward liquidity-sensitive areas, with Financial Services (+1.38%), Real Estate (+1.77%), and Communication Services (+1.15%) outperforming, while Technology (-1.74%) and Utilities (-2.00%) lagged [0]. The policy coordination with Treasury funding needs provides greater operational flexibility for government cash management.
Critical factors to monitor include inflation trends, Treasury market functioning, banking sector health, and the Fed’s communication consistency regarding this policy shift’s permanence versus temporary nature. The elevated market valuations, with SPY trading at a 28.80 P/E ratio near yearly highs [0], suggest markets have already priced in significant policy support, creating potential sensitivity to any policy surprises or economic data deviations.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
