In-depth Investment Research Report on the RISC-V Architecture AI Chip Industry
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Based on the latest data and market information I have collected, I will provide you with a systematic and comprehensive investment analysis report on the RISC-V AI chip industry.
In January 2026, the global semiconductor industry witnessed a historic moment — RISC-V officially captured
In terms of market size, according to Mordor Intelligence data, the RISC-V technology market size reached
- Geopolitical sovereignty needs: Against the backdrop of Sino-US tech competition, players in China, India, Europe and other regions are accelerating their shift to open-source instruction set architectures to build technology stacks not affected by Western export controls[1]
- Improved technological maturity: The latest technological breakthroughs in late 2025 enabled the deployment of out-of-order execution RISC-V cores, with single-threaded performance comparable to high-end laptop processors[4]
- Improved software ecosystem: The RISC-V Software Ecosystem (RISE) project supported by Alphabet ensures that Android and mainstream Linux distributions treat RISC-V as a first-class architecture[4]
The technological evolution of RISC-V presents clear characteristics of “three main tracks”:
| Evolution Direction | 2025-2026 Progress | 2028 Outlook |
|---|---|---|
Industry Specialization |
Early deployment of RVA23 server-level profiles initiated | RVA30 unifies three AI extensions: matrix, vector, and tensor |
High-Performance AI-Oriented |
ESWIN EIC7702X launched; the first RISC-V AI PC reaches 50 TOPS | Deep integration of vector processing units and tensor processing units |
Ecosystem Industrialization |
81 extension standards integrated; RVA23-Automotive ISO certification obtained | Compatibility certification system improved; fragmentation issues avoided |
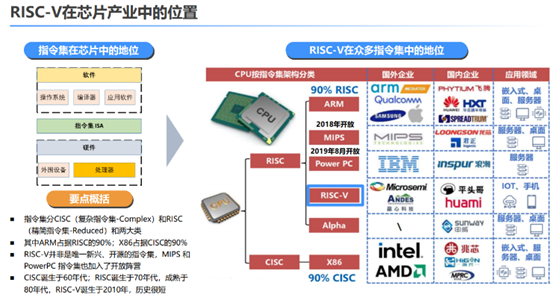
The competition among CPU architectures is essentially a dispute over the design philosophy of
| Feature Dimension | x86 (CISC) | ARM (RISC) | RISC-V (Open RISC) |
|---|---|---|---|
Instruction Set Type |
Complex Instruction Set, single instruction has powerful functions | Reduced Instruction Set, high execution efficiency | Reduced Instruction Set, open-source and customizable |
Licensing Model |
Proprietary to Intel/AMD, restricted licensing | Licensed by ARM, relatively high fees | Open-source and free, no licensing fees |
Power Consumption Characteristics |
Relatively high power consumption, suitable for desktops/servers | Low power consumption, suitable for mobile devices | Flexible power consumption adjustment, covers all scenarios |
Customization Degree |
Almost no customization possible | Limited customization capability | Fully customizable, modular architecture |
Software Ecosystem |
Decades of accumulation, mature and complete | Mobile ecosystem-dominated, expanding | Rapidly maturing, AI ecosystem to be improved |
-
Openness and Independent Controllability: As an open-source instruction set architecture, RISC-V enables enterprises to achieve “technology equality”[5], unlike x86 or Arm which are subject to the private property of specific enterprises
-
AI Customization Advantage: RISC-V’s modular architecture allows designers to customize chips according to specific workloads, adding custom instructions and extensions, which is more flexible than proprietary architectures[3]
-
Performance Catch-Up Trend: Richard Wawrzyniak, chief analyst at SHD Group, pointed out that the performance gap between RISC-V and existing competitors is expected to be largely closed byearly 2027[3]
In the field of AI computing, the three architectures present a differentiated competitive landscape:
- Strengths: Profound software ecosystem, mature toolchain, wide range of industry applications
- Weaknesses: Relatively high power consumption, bloated architecture (legacy burden), restricted customization
- AI Layout: Strengthen CPU-integrated NPU, integrate Xe-LP GPU units
- Strengths: Excellent energy efficiency ratio, mobile ecosystem-dominated, Apple M-series chips verify performance upper limit
- Weaknesses: High licensing fees, legal disputes between Qualcomm and ARM
- AI Layout: Qualcomm acquires Ventana Micro Systems to build the “Oryon-V” roadmap[4]
- Strengths: Zero licensing fees, fully customizable, geopolitically friendly, flexible AI acceleration extensions
- Weaknesses: Software ecosystem still improving, high-performance products just starting
- AI Layout: Alibaba’s T-Head Hangzhou 800/Yitian 700+, Tenstorrent Ascalon-X, Meta MTIA
In late 2025, two major strategic initiatives reshaped the enterprise landscape:
-
Qualcomm’s Acquisition of Ventana: Qualcomm completed the acquisition of Ventana Micro Systems, a leader in high-performance RISC-V cores, for$2.4 billion, which is widely regarded as “declaring independence from Arm”[4]
-
Meta’s Shift to RISC-V: After acquiring AI startup Rivos, Meta began to restructure its Meta Training and Inference Accelerator (MTIA) based on the RISC-V architecture, with a30% increase in performance per watt[4]
This trend indicates that for large AI laboratories and cloud service providers, RISC-V provides a path to “vertical integration” that was previously too costly or legally complex.
China has become an important hub for the RISC-V industry; according to data, the Asia-Pacific region held a
| Enterprise | RISC-V Products | Application Fields | Development Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
Alibaba’s T-Head |
Xuantie C930/910, Hangzhou 800/Yitian 700+ | AI inference, cloud servers, IoT | Mass production and commercialization |
Spacemit |
K1, K3 (upcoming release) | Edge-side AI, robotics, AI PCs | Mass production ramp-up |
HiSilicon (Huawei) |
Ascend series (AI acceleration) | Data centers, AI training | Independent and controllable |
Allwinner Technology |
D1, D1-H, T527 | AIoT, smart home | Mass production and commercialization |
CoreTek Microelectronics |
BT895X platform | Wireless audio, TWS earphones | Mass production and commercialization |
Verisilicon |
RISC-V IP licensing services | IP licensing, design services | Ecosystem construction |
As a leader in the domestic RISC-V ecosystem, Alibaba’s T-Head has formed a complete “edge-cloud integrated” chip product matrix:
- Cloud-Side Inference: Hangzhou 800 and the next-generation inference chip (Yitian 700+), with measured ResNet50 computing power reaching125TOPS, power consumption of 350W, and performance close to NVIDIA H20[6]
- Terminal/Edge: Xuantie series RISC-V processor IP and Yuzhen series SoC chips
- Technological Breakthrough: Launched the 3GHz high-performance core “Yeying” in 2025, breaking the stereotype that “RISC-V = low power consumption”
- The Xuantie processor ecosystem has covered over 150 customers, with more than500 licenses
- The total revenue of ecosystem partners exceeded CNY 80 billion in 2024
- Cumulative registered users exceed 200,000[6]
As a startup focusing on RISC-V AI chips, Spacemit has shown strong development momentum:
- Series B financing scale: hundreds of millions of RMB
- Investors: China Internet Investment Fund, Agricultural Bank of China AIC, Beijing Artificial Intelligence Industry Investment Fund, Beijing State-Owned Assets Management Shunxi Fund, Huaxia Hengtian, Guangyuan Capital, etc.[5]
| Product | Status | Core Indicators | Target Market |
|---|---|---|---|
K1 |
Mass-produced | 150,000 units shipped; the highest volume of mass-produced high-performance RISC-V chips in China | Edge-side AI applications |
K3 |
To be released in January 2026 | Targeting edge-side large models with 30B parameters | Edge-side intelligence |
3rd-Generation Cloud-Side Chip |
To be launched in H2 2026 | Targeting cloud computing server CPUs | Cloud-side AI inference |
-
Full-Stack Independent R&D Capability: One of the rare teams in China with full-stack independent R&D and commercial mass production capabilities from instruction set, IP core, chip, software to complete machine[5]
-
Technological Independence and Controllability: Insists on independent R&D of both CPU cores and AI cores, avoiding reliance on suppliers
-
Excellent Team Background: Core team members come from Alibaba’s T-Head, HiSilicon (Huawei), and Allwinner Technology; founder Chen Zhijian is a PhD from Zhejiang University and a recipient of national talent program support[5]
-
Edge-side AI Devices: In the market for edge-side large models with less than 30B parameters, RISC-V’s customization advantage is obvious
- Spacemit’s K3 chip is precisely positioned for this niche market[5]
- Cost advantage: 20-30% lower than ARM solutions with equivalent performance
-
AIoT and Edge Computing: Smart terminal devices sensitive to power consumption and cost
- Market penetration rate reached 26.12% (2025)[2]
- Allwinner Technology, CoreTek Microelectronics, etc. have achieved large-scale mass production
-
Automotive Electronics: The RVA23-Automotive specification is expected to obtain ISO 26262 ASIL-D certification
- Strong demand for autonomous driving domain controller chips
- LionTech has provided a full-process testing solution for T-Head[6]
-
Mature Software Ecosystem: The maturity of the RISC-V ecosystem is expected to approach that of Arm64 by 2027[7]
- Mainstream operating systems such as Ubuntu, Debian, and OpenEuler already provide stable support
- System software stacks such as FlagOS are accelerating adaptation
-
Data Center Penetration: The application of RISC-V in data centers will grow at a60.9% CAGRthrough 2031[2]
- “Chiplet” design will be key: RISC-V management cores paired with dedicated AI accelerators
- Driven by internal chip projects of cloud computing vendors such as Meta and Alibaba
-
AI PC Market: The second-generation RISC-V laptops are expected to launch in H2 2026
- Battery life exceeds current x86 benchmarks
- Driven by computing power demand for local AI Agents
- Shipment volume of RISC-V SoC chips is expected to reach 20 billion units
- SoC market penetration rate exceeds 25%
- Market share in six core markets (consumer, computer, automotive, data center, industrial, network) will be between 26%-39%[1]
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) training scenarios: NVIDIA GPU ecosystem still dominates
- Traditional PC desktop market: Windows ecosystem is tied to x86
- Complex server workloads: x86 still holds an advantage due to ecosystem inertia
RISC-V Replacement Path (from easiest to hardest):
Level 1: IoT/AIoT → Large-scale replacement already achieved ✓
│
Level 2: Edge-side AI/Embedded → Penetration in progress ✓
│
Level 3: AI PC/Consumer Electronics → Critical window 2026-2027 →
│
Level 4: Data Center/Server → Ecosystem breakthrough 2027-2030 →
│
Level 5: HPC/AI Training → Long-term competition requires architectural innovation
- RISC-V is a “key opportunity for the country’s computing power chips to overtake by changing lanes”[5]
- Clear trend of edge-side intelligence (“Everything will have a local large model”)
- Mid-to-short-term market size of approximately CNY 318 billion, long-term trillion-dollar market[5]
- Rare full-stack independent R&D capability in China, avoiding “stuck neck” risks
- High-performance RISC-V CPU core performance exceeds 16 points/GHz SPECINT2006[5]
- Self-developed Spacemit homogeneous fusion technology, highlighting AI chip advantages
- Founder Chen Zhijian: PhD from Zhejiang University, recipient of national talent program support, began research on domestic processors in 2006[5]
- Core team: From well-known enterprises such as Alibaba’s T-Head, HiSilicon (Huawei), and Allwinner Technology
- R&D personnel account for >80%, master’s and doctoral degree holders account for >50%[5]
- 150,000 K1 chips mass-produced, the highest volume of mass-produced high-performance RISC-V chips in China[5]
- Clear product iteration rhythm: Launch one generation of chips per year, with 4-8 times improvement in CPU/AI computing power
- Clear commercial path: Starting from edge-side, gradually penetrating into cloud-side and high-end applications
| Indicator | 2025 (Estimated) | 2026 (Projected) | 2027 (Projected) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Scale | CNY 20-30 million | CNY 60-100 million | CNY 200-300 million |
| Gross Margin | 30-35% | 35-40% | 40-45% |
| R&D Investment Ratio | 50%+ | 40%+ | 35%+ |
| Chip Shipment Volume | 150,000+ K1 units | 500,000+ units (K1+K3) | 1.5 million+ units |
Referring to valuation levels of similar AI chip companies:
- High R&D investment intensity, long profit cycle (chip companies usually take 7-8 years to reach CNY 100 million in revenue)
- Spacemit pursues exponential revenue growth (targeting 3x growth per year)[5]
- Series B valuation in the primary market should be 10-15x PS(based on high revenue growth expectations)
- Valuation premium is reasonable considering track popularity and team background
- Risk of dilution from subsequent financing
- Risk of low yield in mass production
- Risk of intensified market competition
- Risk of industry valuation correction
| Investment Dimension | Assessment | Weight |
|---|---|---|
Track Attractiveness |
★★★★★ Domestic replacement + AI wave + Rise of RISC-V | 30% |
Technological Barriers |
★★★★☆ Full-stack independent R&D, excellent team | 25% |
Commercialization Capability |
★★★★☆ Leading mass production, clear path | 25% |
Valuation Rationality |
★★★☆☆ Valuation in primary market is relatively high | 20% |
- Long-Term Layout: As a core target in the RISC-V track, it is worthy of long-term tracking
- Key Nodes to Watch: January 2026 K3 chip release, progress of cloud-side chips in H2 2026
- Exit Paths: IPO on STAR Market or strategic acquisition by internet giants, automakers, etc.
AI chip and RISC-V technologies update rapidly, and products may be quickly replaced or outperformed
- Rise of ARM PC ecosystem (Qualcomm Oryon, Apple Silicon)
- x86 counterattack (continuous innovation from Intel and AMD)
- Intensified domestic competition (Alibaba’s T-Head, other startups)
- Software ecosystem is still improving, which may affect product promotion
- Dependence on upstream manufacturing processes (such as SMIC)
- Restricted access to advanced manufacturing processes
- Uncertainty in export controls
- Technological Independence and Controllability: Full-stack independent R&D reduces supply chain risks
- Scenario Differentiation: Focus on edge-side AI to avoid direct competition with giants
- Policy Support: Domestic computing power chips receive policy support
- Capital Support: Endorsement by top institutions ensures subsequent financing
-
The RISC-V architecture is reshaping the global computing power landscape; capturing 25% market share in 2026 marks the official formation of the “third pole”
-
In the era of AI computing, RISC-V has structural advantages: open and customizable, excellent energy efficiency ratio, geopolitically friendly, and is expected to replace ARM/X86 in scenarios such as edge-side AI and edge computing
-
Domestic RISC-V chip players are facing a strategic opportunity period; Alibaba’s T-Head has verified the commercialization path, and rising stars such as Spacemit are emerging
-
Spacemit has scarce investment value: with full-stack independent R&D capability, excellent team background, and clear commercial path, it is a core target in the RISC-V AI chip track
- Pay attention to the release of K3 chip and market validation of 30B edge-side large models
- Breakthrough of RISC-V in the AI PC market
- Continued financing enthusiasm in the industry
- Maturity of RISC-V ecosystem approaches that of Arm64
- Accelerated penetration in data centers
- Industry integration may occur, and leading positions will be established
- RISC-V is expected to become one of the global mainstream computing systems
- Domestic computing power chips achieve independence and controllability
- Trillion-level market scale is formed
[1] EET-China - “Top 10 Technology Trends in the Global Semiconductor Industry in 2026” (https://www.eet-china.com/news/202512172329.html)
[2] Mordor Intelligence - “RISC-V Tech Market Share, Size & Growth Outlook to 2031” (https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-re
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
