Deteriorating Indonesian Finances and Currency Crisis: In-Depth Analysis of Impacts on Investors
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features

About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
Now let me generate a comprehensive integrated analysis report for you:
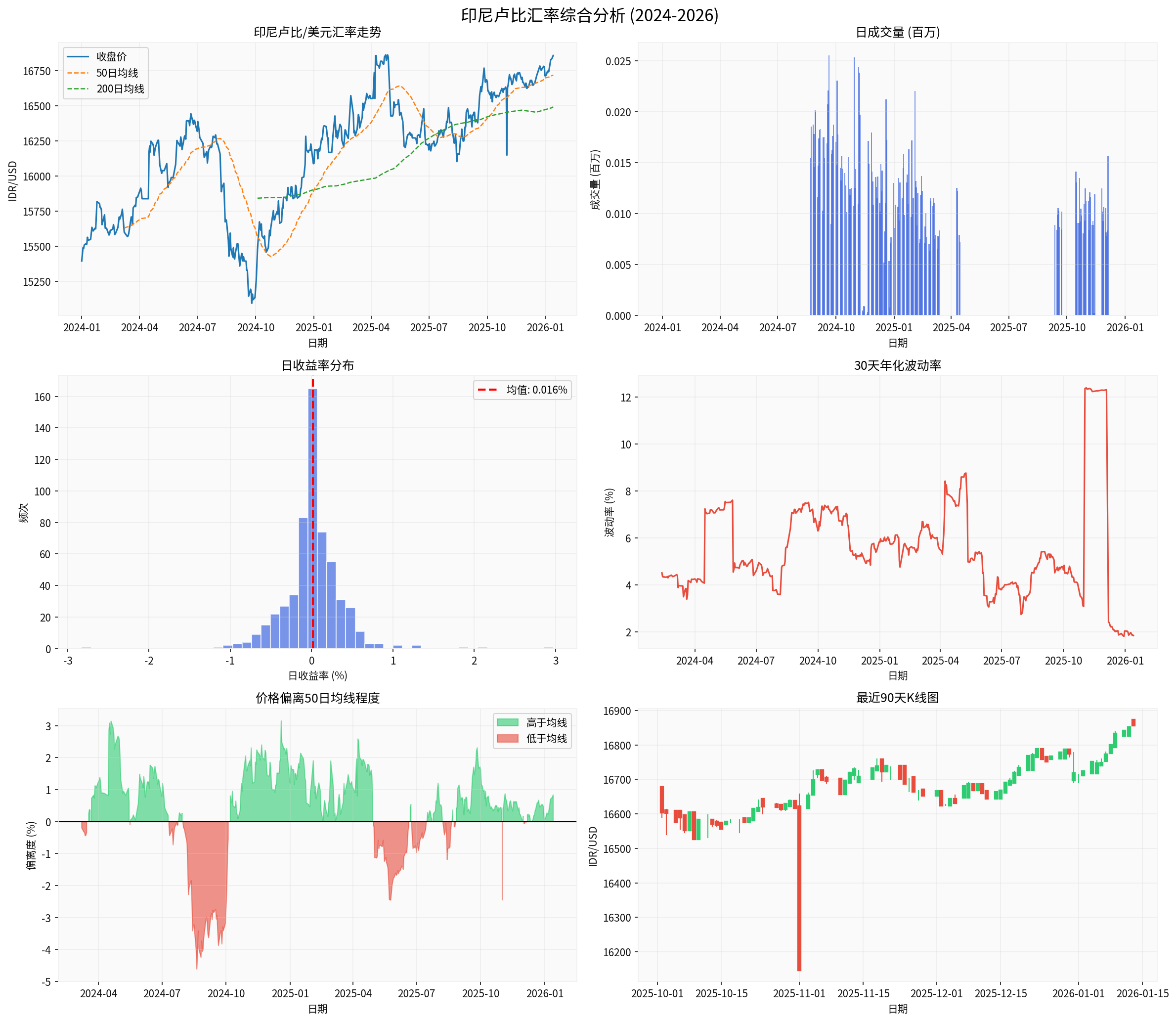
As of January 13, 2026, the Indonesian rupiah closed at
| Indicator | Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Latest Closing Price | 16,860 IDR/USD | Near historical low |
| YTD Depreciation | Approximately 4.79% | Weak performance |
| 90-Day Annualized Volatility | 7.28% | Increased volatility |
| Deviation from 50-Day Moving Average | +0.83% | Slightly above the moving average, facing technical pressure |
2025 fiscal data released by the Indonesian government shows [1][2]:
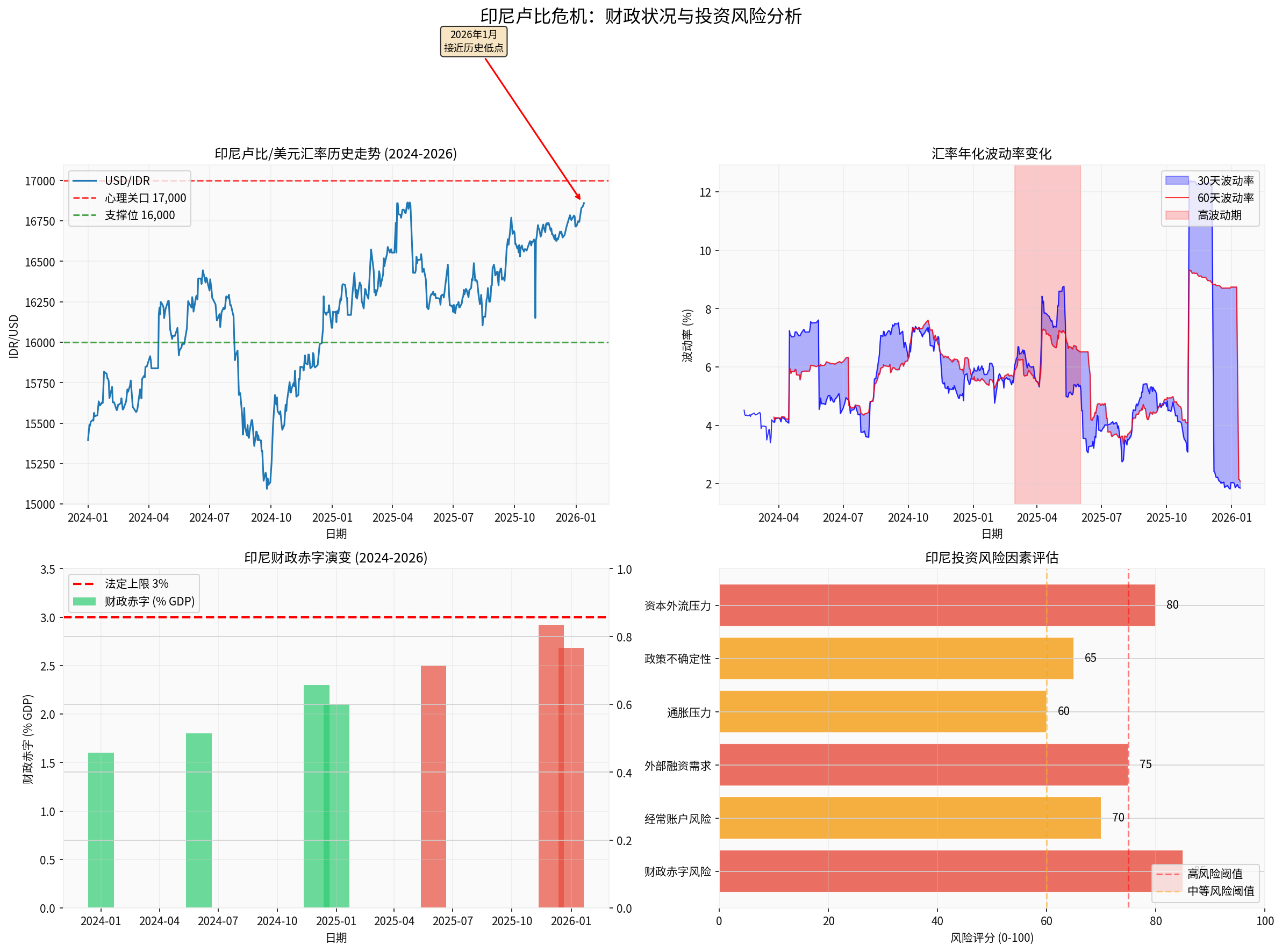
- The budget deficit reached IDR 695.1 trillion, accounting for2.92% of GDP
- This level is one of the worst deficits in more than two decades
- A year-on-year surge of 36.5% (up from IDR 509.2 trillion)
- Approaching the statutory upper limit of 3%warning threshold
- Although the government’s 2026 target is lowered to 2.68%, analysts believe it may be difficult to achieve
Bank Indonesia (BI) has adopted multi-faceted intervention measures [1]:
| Intervention Market | Scope |
|---|---|
| Offshore Market | Non-deliverable forward (NDF) foreign exchange markets in Asia, Europe, and the Americas |
| Onshore Market | Spot foreign exchange, NDF, and government bond markets |
| Policy Communication | Emphasize maintaining the exchange rate in line with fundamental value |
- Adequacy of foreign exchange reserves is being tested
- Intervention costs continue to rise
- A tug-of-war with capital outflow pressure
Based on the latest market data, we have constructed a risk assessment framework [0]:
| Risk Factor | Score (0-100) | Risk Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Deficit Risk | 85 |
🔴 High | Deficit approaching statutory upper limit |
| Capital Outflow Pressure | 80 |
🔴 High | Foreign investors continue to withdraw |
| External Financing Demand | 75 |
🔴 High | Pressure from USD bond issuance |
| Current Account Risk | 70 | 🟠 Medium-High | Pressure from trade deficit |
| Policy Uncertainty | 65 | 🟠 Medium-High | Coordination between fiscal policy and central bank |
| Inflation Pressure | 60 | 🟠 Medium | Import cost pass-through |
- Direct impact: Bond prices fall, yields rise
- Foreign investors have been net sellers of Indonesian government bonds (SBN) since September 2025 [1]
- The Indonesian government issued USD 2.7 billion in dollar bonds on January 12, 2026 to supplement USD liquidity [2]
- The Indonesian stock market faces pressure from foreign capital outflows
- Currency depreciation deals a double blow to import-dependent enterprises
- Export-oriented enterprises relatively benefit from improved exchange rate competitiveness
- Indonesian exposure may drag down the overall performance of the fund
- Need to evaluate the weight and risk contribution of Indonesia in the portfolio
- Consider rebalancing regional allocation
- Foreign exchange reserve buffer: Bank Indonesia holds a considerable scale of foreign exchange reserves
- Policy coordination space: The Ministry of Finance has committed to complying with the 3% deficit cap
- USD supply supplement: Introduce external funds through USD bond issuance
-
Fundamental issues unresolved:
- Structurally high fiscal deficit
- Slowing economic growth
- Persistent trade deficit
-
External environmental pressure:
- Rising geopolitical uncertainty
- Rising global risk aversion
- Relative strength of the US dollar
-
Self-reinforcing market expectations:
- Damaged investor confidence
- Vicious cycle of capital outflows
- Implement a credible fiscal consolidation plan
- Maintain central bank policy independence
- Improve economic fundamentals to restore investor confidence
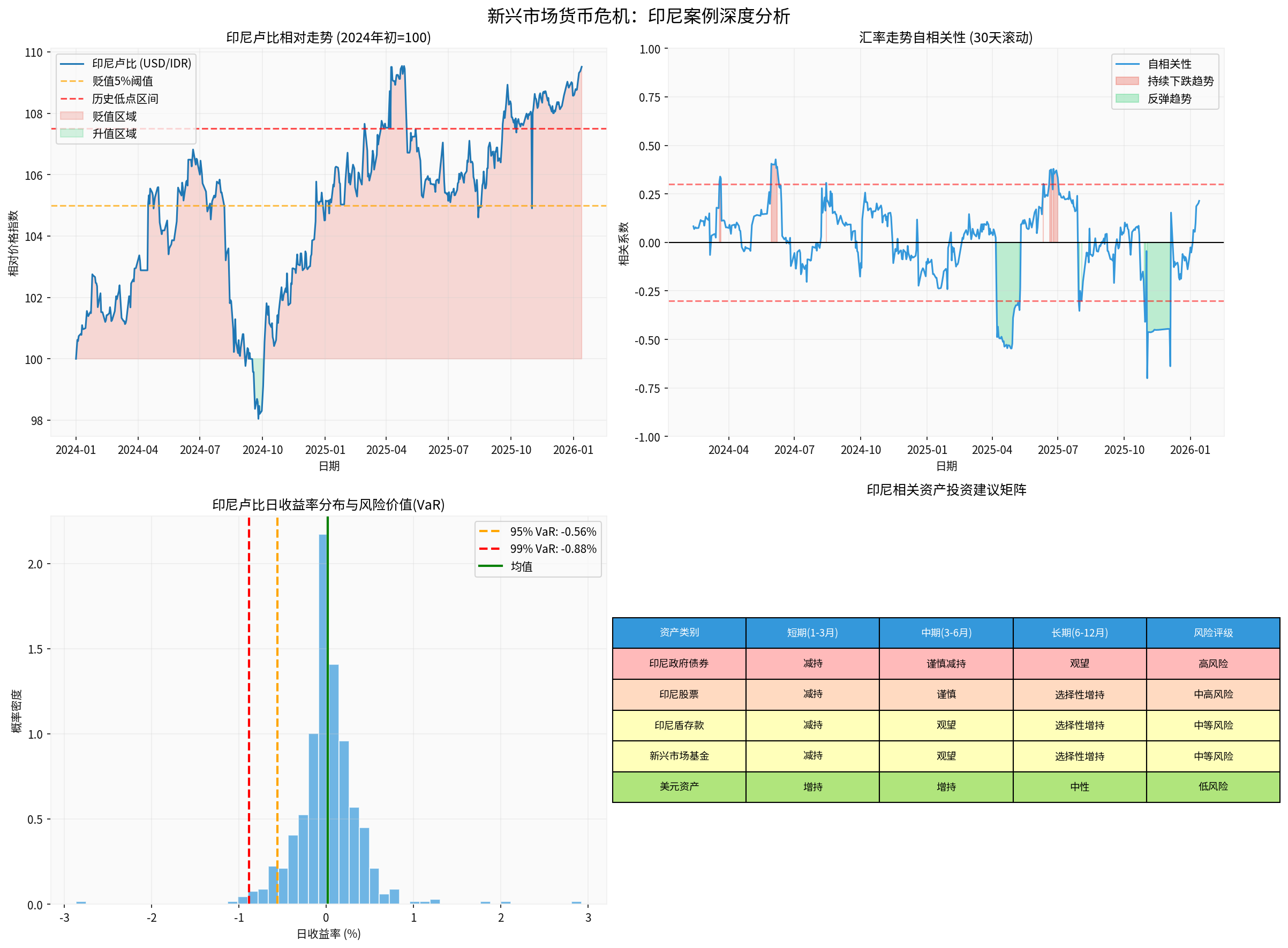
| Asset Class | Short-Term (1-3 Months) | Medium-Term (3-6 Months) | Long-Term (6-12 Months) | Risk Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesian Government Bonds | 🔴 Reduce Holdings | 🔴 Reduce Holdings | 🟡 Hold | High Risk |
| Indonesian Stocks | 🔴 Reduce Holdings | 🟠 Cautious | 🟢 Selective Increase | Medium-High Risk |
| Rupiah Deposits | 🔴 Reduce Holdings | 🟡 Hold | 🟢 Selective Increase | Medium Risk |
| Emerging Market Funds | 🔴 Reduce Holdings | 🟡 Hold | 🟢 Selective Increase | Medium Risk |
| USD Assets | 🟢 Increase Holdings | 🟢 Increase Holdings | 🟡 Neutral | Low Risk |
- Evaluate exposure scale: Calculate the proportion of Indonesian assets in the portfolio
- Consider currency hedging: Hedge rupiah exposure to reduce exchange rate risk
- Diversified investment: Increase exposure to other emerging markets to diversify risks
- Wait for clearer signals: Consider increasing holdings only after fiscal consolidation measures are introduced
- Focus on valuation levels: Indonesian asset valuations have already priced in some pessimistic expectations
- Batch position-building strategy: Avoid one-time large investments
- Review fund strategies: Understand the fund’s specific exposure to Indonesia
- Consider defensive allocation: Increase allocation to low-volatility emerging markets
- Monitor fund manager adjustments: Observe whether fund managers actively adjust Indonesian exposure
According to the latest market research [3][4]:
- Emerging markets as a whole performed strongly in 2025, with the local currency bond index rising 19.3%
- However, there is significant divergence among countries, and Indonesia lags behind due to fiscal issues
- In comparison, the Chilean peso, South African rand, and Thai baht have performed more stably
- The US Dollar Index remains in a historically high range [3]
- The Federal Reserve is expected to continue cutting interest rates in 2026, which may ease pressure on emerging markets
- However, the decline in USD hedging costs may limit the room for a sharp USD correction
- The Indonesian government successfully controls the deficit within 3% of GDP
- Central bank interventions effectively stabilize the exchange rate
- The rupiah fluctuates within the range of 16,500-17,500
- The fiscal deficit breaks through the statutory 3% upper limit
- Capital outflows intensify, and the central bank is forced to raise interest rates sharply
- The rupiah breaks below the historical low of 17,500
- Fiscal consolidation measures take effect, and the deficit narrows significantly
- External environment improves, and the USD weakens
- The rupiah stabilizes and rebounds below 16,000
Based on the latest technical indicators [0]:
| Indicator | Value | Signal Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Current Price | 16,860 | Near key resistance level |
| 20-Day Moving Average | 16,775 | Price slightly above the moving average |
| 50-Day Moving Average | 16,720 | Medium-term trend is weak |
| 200-Day Moving Average | 16,494 | Long-term trend is downward |
| RSI(14) | Approximately 55 | Neutral-weak |
| MACD | Negative | Downward momentum |
-
Fiscal deterioration is the root cause: The 2.92% deficit level has approached the statutory upper limit, and investors have concerns about debt sustainability [2]
-
Limited effectiveness of central bank intervention: Although the pace of depreciation has slowed, structural issues cannot be resolved [1]
-
Investors need to respond cautiously: It is recommended to reduce short-term exposure and wait for clearer market signals
-
Growing divergence in emerging markets: Emerging market investments in 2026 need to pay more attention to country selection and risk management
Investors should closely monitor the following indicators:
- Actual 2026 fiscal deficit data of Indonesia
- Trend of changes in foreign exchange reserves
- Changes in foreign investors’ holdings of Indonesian bonds
- Federal Reserve interest rate policy trends
- US Dollar Index trends
[0] Gilin AI Financial Database - Indonesian Rupiah Exchange Rate Data and Technical Analysis
[1] Reuters - “Indonesian central bank to continue intervening to defend depreciating rupiah” (January 14, 2026) https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/indonesia-central-bank-continue-intervening-defend-depreciating-rupiah-2026-01-14/
[2] Katadata DataBoks - “Indonesia’s State Budget Deficit Hits Rp695 Trillion in 2025, Reaching 2.92% of GDP” (January 9, 2026) https://databoks.katadata.co.id/en/economics-macro/statistics/6960968c30069/indonesias-state-budget-deficit-hits-rp695-trillion-in-2025-reaching-292-of-gdp
[3] Franklin Templeton - “2026 outlook: Cross-country divergences” https://www.franklintempleton.com/articles/2025/brandywine-global/2026-outlook-cross-country-divergences
[4] State Street - “Market Signals and Shifts: What to watch in 2026” https://www.statestreet.com/content/statestreet/ie/en/insights/market-outlook-2026
[5] BCA Research - “2026 Indonesia Economic Outlook” https://www.bca.co.id/-/media/Feature/Report/File/S8/Laporan-Riset-Ekonomi/2025/12/2026-indonesia-economic-outlook-inching-towards-higher-growth-19-december-2025.pdf
[6] Business Today Malaysia - “Rupiah Near Historic Low As Bank Indonesia Steps Up Market Interventions” (January 14, 2026) https://www.businesstoday.com.my/2026/01/14/rupiah-near-historic-low-as-bank-indonesia-steps-up-market-interventions/
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
