ICT/SMC Trading Concepts Refutation: Evidence-Based Market Microstructure Analysis
Unlock More Features
Login to access AI-powered analysis, deep research reports and more advanced features
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
This analysis is based on the Reddit post [1] “A Clean ICT Refutation, Evidence not Insults” published on November 11, 2025, which systematically critiques popular trading concepts from Inner Circle Trader (ICT) and Smart Money Concepts (SMC). The author presents evidence-based arguments grounded in market microstructure theory, challenging the notion of centralized price delivery algorithms in favor of order flow dynamics and liquidity imbalances as the primary drivers of price movements [1]. The refutation emphasizes developing unique, testable trading edges rather than following saturated, discretionary narratives that lack empirical validation.
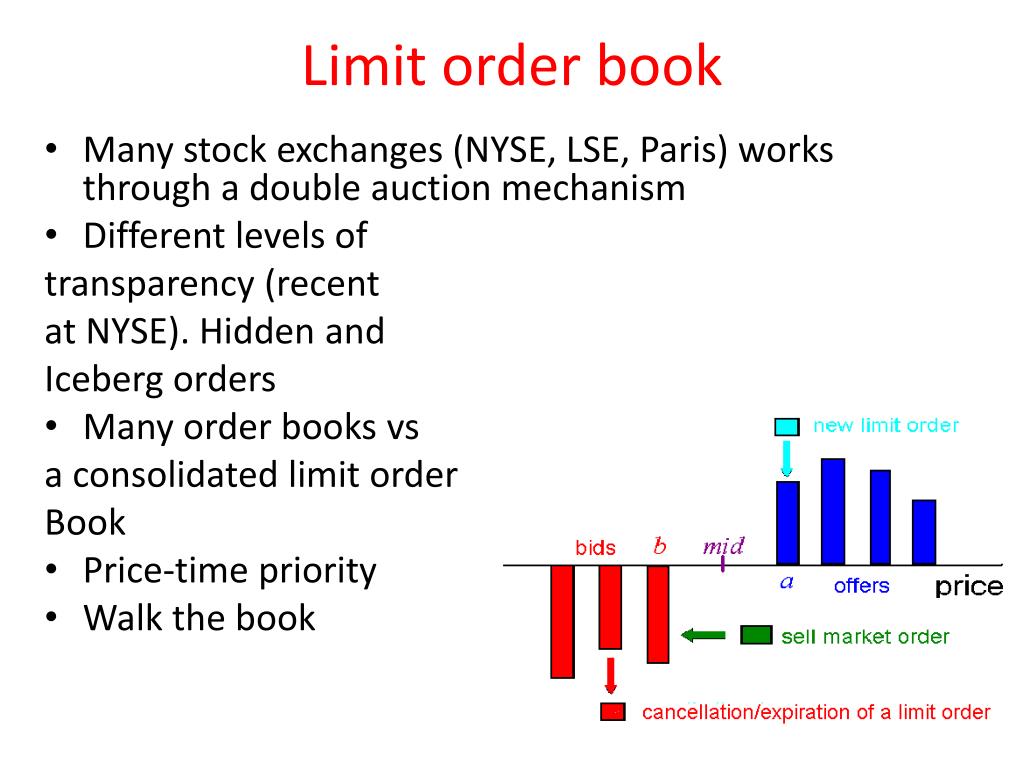
The core of the refutation centers on contrasting ICT/SMC concepts with established market microstructure research. ICT theory promotes the Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm (IPDA) as a centralized system governing price delivery, claiming institutions systematically target liquidity pools through predictable mechanisms [3][4]. However, extensive academic research demonstrates that price formation emerges from decentralized order matching processes in limit order books (LOBs), not from centralized algorithms [2].
Cont et al.'s seminal work establishes a linear relationship between order flow imbalance and price changes, with slopes inversely proportional to market depth [2]. This evidence-based framework explains price movements through measurable supply-demand dynamics rather than mysterious delivery algorithms. The research shows that order flow imbalance can be quantified at multiple LOB levels, with price impact being predictable based on imbalance magnitude [2].
Academic studies using frameworks like LOBFrame have successfully modeled LOB dynamics without invoking centralized algorithms [2]. These models achieve predictive accuracy by learning patterns in order flow, spread dynamics, and liquidity provision - all measurable microstructural phenomena. The research on 15 NASDAQ stocks revealed heterogeneous liquidity patterns that vary significantly across different market conditions and asset classes, contradicting the notion of a universal delivery algorithm [2].
The Reddit author’s emphasis on developing “unique, testable edges” aligns with quantitative trading research [1]. Academic studies consistently show that successful trading strategies are based on statistical arbitrage of microstructural inefficiencies, exploitation of predictable patterns in order flow, and risk management based on empirical volatility measures [2][5].
The critique of “saturated, discretionary narratives” reflects genuine concerns in the trading education space [1]. When concepts like IPDA become widely adopted without empirical validation, their effectiveness diminishes due to crowded trades reducing profitability, self-fulfilling prophecies creating artificial patterns, and reduced alpha generation from common knowledge [6].
Research confirms that liquidity distribution is highly dynamic and influenced by multiple factors including order flow imbalance, market depth, and participant behavior [2]. Market orders consume liquidity while limit orders provide it, affecting transaction costs and price impact. This creates a complex ecosystem where price movements arise from the continuous interaction of these forces rather than predetermined delivery mechanisms [2].
HFT strategies exploit market microstructure patterns rather than following predetermined delivery algorithms [2]. These strategies capitalize on fleeting inefficiencies in order flow, spread dynamics, and liquidity provision - all measurable phenomena that can be quantified and tested empirically.
The refutation highlights a significant gap between academic market microstructure research and retail trading education. While academics have developed sophisticated models of LOB dynamics [2][6], retail trading communities often gravitate toward simplified narrative-based explanations that lack empirical validation [1][3][4].
Posts like this contribute to market efficiency by reducing information asymmetry between retail and institutional traders [1]. By promoting evidence-based trading strategies and challenging misconceptions, they help level the playing field and potentially reduce systematic losses from following unproven methodologies.
The debate represents a broader trend toward evidence-based trading education. As more traders gain access to academic research and quantitative tools, the demand for scientifically validated trading approaches increases [1][2][5]. This shift could lead to more sophisticated retail trading strategies and better risk management practices.
Understanding true market microstructure rather than relying on unproven algorithms improves risk management through better comprehension of liquidity dynamics during market stress, price impact of large orders, and market depth and resilience factors [2][6].
The widespread adoption of unvalidated trading concepts like IPDA poses significant risks to retail traders who may base their strategies on flawed assumptions about market mechanics [1][3][4]. This could lead to systematic losses and poor risk management decisions.
The technical nature of market microstructure research creates barriers to entry for many retail traders. Understanding LOB dynamics, order flow imbalance, and liquidity mechanics requires significant computational resources and data access that may not be readily available to all market participants [2][5].
There are opportunities for developing educational platforms that bridge the gap between academic research and practical trading applications [1][5]. By making complex microstructural concepts accessible, these platforms could help traders develop more robust strategies.
Advances in computing power and data availability are making sophisticated market microstructure analysis more accessible to retail traders [2][5]. This creates opportunities for developing tools that can provide real-time LOB analysis and order flow metrics.
The emphasis on testable, evidence-based strategies opens opportunities for traders who can develop quantitative edges based on market microstructure inefficiencies [1][2][5]. These edges may be more sustainable than narrative-based approaches.
Research confirms that price formation occurs through continuous double auction mechanisms in limit order books, not through algorithmic delivery systems [2][6]. Price changes are driven by submission and cancellation of orders, creating self-organized processes that can be modeled and predicted.
Liquidity distribution is highly dynamic and influenced by multiple factors including order flow imbalance, market depth, and participant behavior [2]. Market orders consume liquidity while limit orders provide it, affecting transaction costs and price impact in measurable ways.
Successful trading strategies should be based on falsifiable predictions, statistical validation against appropriate benchmarks, and risk-adjusted returns that account for transaction costs and market impact [2][5].
Evidence-based trading approaches focus on statistical arbitrage of microstructural inefficiencies, exploitation of predictable patterns in order flow, and risk management based on empirical volatility measures [2][5].
Effective implementation of market microstructure-based strategies requires access to high-quality LOB data, significant computational infrastructure, and real-time processing capabilities [2][5].
Traders should prioritize understanding of market microstructure fundamentals, statistical validation methods, and risk management principles over following popular trading narratives without empirical support [1][2][6].
This analysis demonstrates the importance of evidence-based trading education and the value of academic research in developing robust trading strategies. The refutation of ICT/SMC concepts with market microstructure evidence represents a positive development toward more sophisticated and scientifically grounded trading approaches.
Insights are generated using AI models and historical data for informational purposes only. They do not constitute investment advice or recommendations. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
About us: Ginlix AI is the AI Investment Copilot powered by real data, bridging advanced AI with professional financial databases to provide verifiable, truth-based answers. Please use the chat box below to ask any financial question.
