Based on the collected data and information, I will provide you with an in-depth analysis of the differential impact of the ‘aluminum vs. copper debate’ in the air conditioning industry on major enterprises.
The ‘Aluminum vs. Copper Debate’ in the Air Conditioning Industry: Analysis of the Differential Impact of Technical Route Choices on Enterprise Competitiveness
I. Industry Background: Dual Impetus from Cost Pressure and Policy Drivers
1.1 Cost Pressure: Industrial Chain Dilemma Amid Soaring Copper Prices
The Reality of Skyrocketing Copper Prices
: In 2025, global copper prices witnessed a historic rise. The London Metal Exchange (LME) copper price repeatedly hit record highs, exceeding $11,461 per ton; the main contract of Shanghai copper futures stood at the 92,000 yuan/ton mark, with a cumulative increase of over 30% within the year [1].
Cost Structure of the Air Conditioning Industry
: According to industry data, copper, as a core raw material for air conditioners, accounts for
20%-30%
of the total cost of an air conditioner. The copper usage per air conditioner is approximately
6-7 kg
. Based on the current copper price of 92,000 yuan/ton, the cost of copper materials alone is as high as about
600 yuan
.
Economic Viability of Aluminum Substitution
: In contrast, the aluminum price is only
22,000 yuan/ton
. The cost of aluminum materials of the same weight is only 140 yuan, which can save about
460 yuan
per air conditioner, a decrease of
77%
. This is undoubtedly a huge temptation for the air conditioning industry, which has been under continuous profit pressure.
1.2 Policy Drivers: Promotion from National Strategic Level
Resource Endowment Difference
: China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of air conditioners, but its self-sufficiency rate of copper resources is less than
30%
. In 2024, the Chinese air conditioning industry consumed about 2.56 million tons of copper, accounting for 77% of the total copper consumption in the domestic home appliance industry [1]. In sharp contrast, China’s electrolytic aluminum production accounts for
60%
of the world’s total, and the supply of raw materials is completely independent and controllable.
Policy Support
: In March 2025, ten departments including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology jointly issued the “High-Quality Development Implementation Plan for the Aluminum Industry (2025-2027)”, which clearly listed “saving copper with aluminum” as a key direction for expanding aluminum consumption [2]. This elevated “saving copper with aluminum” to the national strategic level.
1.3 Technical Status: Performance Gaps and Solutions
Comparison of Material Properties
:
Thermal Conductivity
: Copper is about 401 W/m·K, aluminum is about 237 W/m·K (less than half of copper) [3]Corrosion Resistance
: The annual corrosion rate of copper is only 0.001 mm, while aluminum is chemically active and prone to oxidationService Life
: The average service life of aluminum tube air conditioners is about 8-10 years, while copper tube air conditioners can reach 15-20 years [3]Welding Process
: The melting point of aluminum is 660°C, much lower than copper’s 1083°C, making it prone to pores and cracks
Technical Progress
: Supporters believe that through structural optimization, process improvement, and material modification, the performance shortcomings of aluminum are being compensated. Leading enterprises have significantly improved the corrosion resistance of aluminum through heat exchange structure innovation, corrosion-resistant substrate design, surface zinc spraying treatment, and coating technology [3].
II. Enterprise Strategy Differentiation: Different Choices of the Three Giants
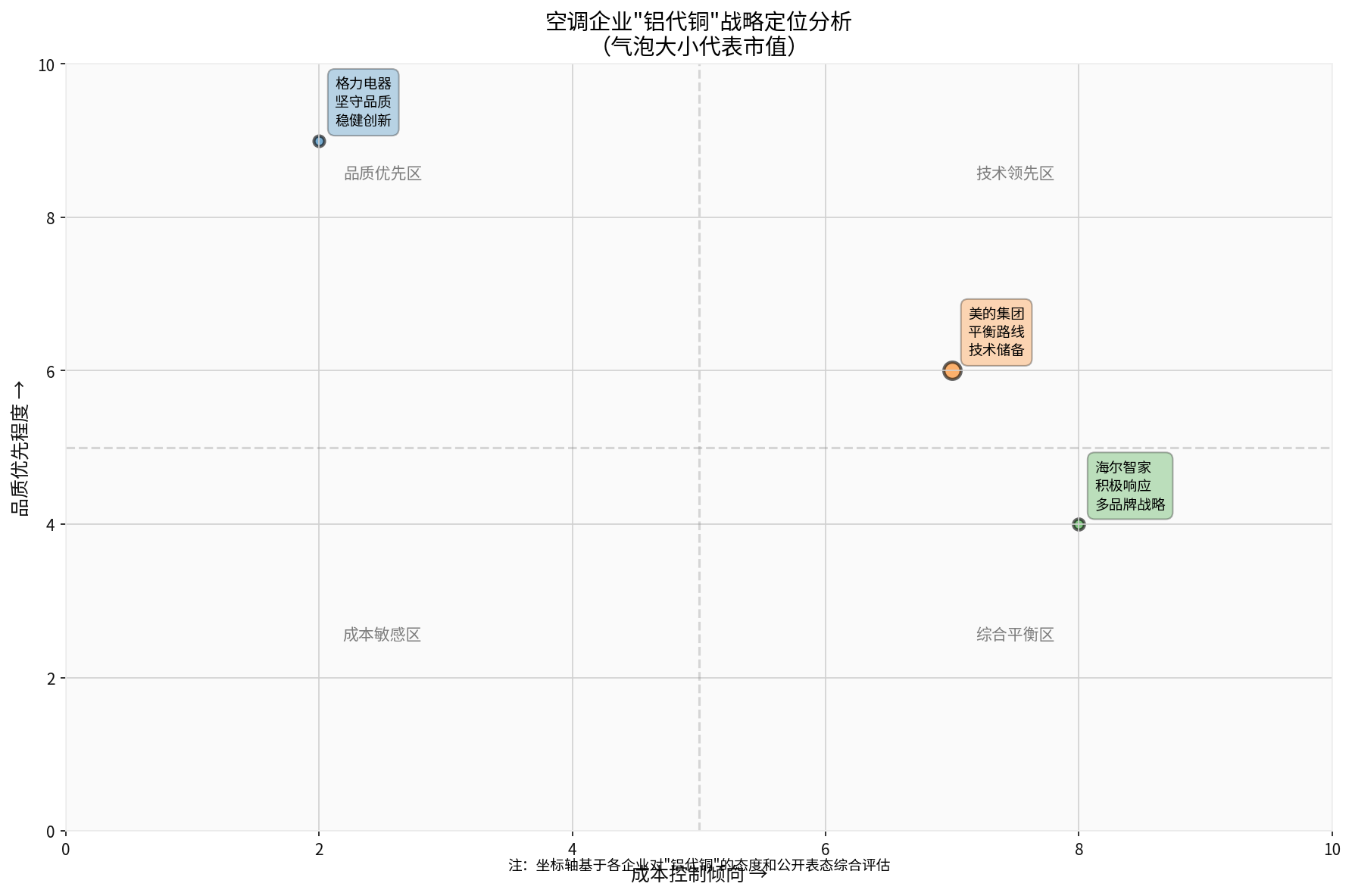
*Figure 1: Analysis of Air Conditioner Enterprises’


